Table Of Content
Intelligent design is an inference from empirical evidence, not a deduction from religious authority. Intelligent design is controversial because it purports to find signs of intelligence in nature, and specifically in biological systems. According to the evolutionary biologist Francisco Ayala, Darwin’s greatest achievement was to show how the organized complexity of organisms could be attained apart from a designing intelligence. Intelligent design therefore directly challenges Darwinism and other naturalistic approaches to the origin and evolution of life. The idea in its current form appeared in the 1980s, and Johnson adopted and developed it after Darwinian evolution came up short, in his view, in explaining how all organisms, including humans, came into being.
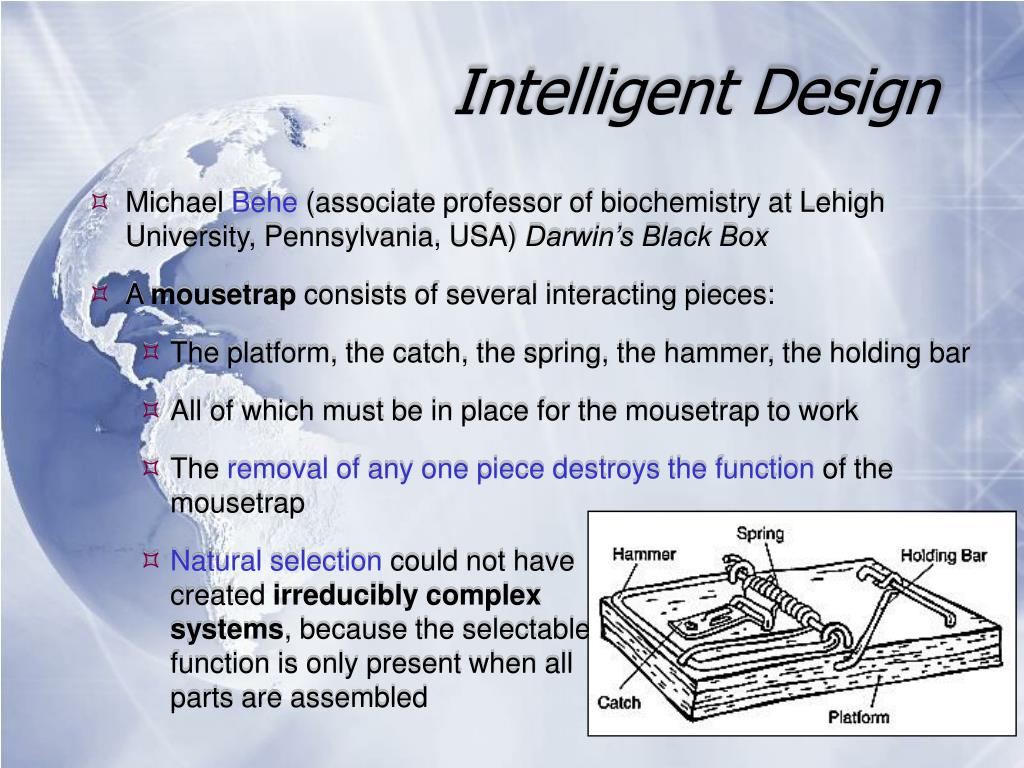
Intelligent design
The real question is whether any “natural” objects—such as galaxies, rocks, trees, or people—also require “intelligent” causes to design them and, if so, whether such causes should be part of any scientific explanations of those objects. Dembski’s idea of “specified complexity” and Behe’s idea of “irreducible complexity” come into play just at this point. ID proponents believe that the scientific toolbox needs to include “design,” an explanatory tool that includes rather than excludes intelligent causation as part of the explanation for how certain things came into existence. Their opponents think the scientific toolbox is large enough as is, without adding “design” to the set. Interestingly, the authors speak explicitly and often about “God” and “special creation” throughout the “Epilogue.” As I say, they were writing before Johnson’s strategy of avoiding all explicitly religious language was implemented. Although I used different terminology in that earlier column, where I spoke about “the distinction between fields of science that are sometimes called ‘historical sciences,’ and other fields that are sometimes called ‘experimental sciences’,” I meant the very same thing.
Is There a Signature in the Cell?
The public has seen that what they are getting from the evolutionary biologists is, on the one hand, less than science. It is over-enthusiastic claims of great accomplishments that are not supported by real, observational, and experimental evidence. I think it is a theory in crisis, but that requires some explanation. That's a possibility that has to be considered also, that there's a commonality not only between chimps and humans, but among all life. And thus this might be pointing to a single evolutionary process, or it might be pointing to the responsibility of a single creator.
Senate Education Committee moves intelligent design bill, other legislation forward - West Virginia MetroNews
Senate Education Committee moves intelligent design bill, other legislation forward.
Posted: Tue, 16 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The Science of Intelligent Design
Parts of The Mystery of Life’s Origin are highly technical, but the overall argument is clear from the concluding chapter and the very important “Epilogue” that follows, and which I invite readers to summarize in the comments if they wish. Basically, the authors argue that we just don’t know very much about the origin of life, that we need to reassess current ideas, and that a design principle might be needed if we want a better answer. In 2004, the school board of Dover, Pennsylvania, voted to require the teaching of intelligent design alongside evolution in science classrooms.
Given that the street is wet (and without additional evidence to decide the matter), one can only conclude that perhaps it rained. Because there are many other possible ways by which the street may have gotten wet. Rain may have caused the streets to get wet; a street cleaning machine might have caused them to get wet; or an uncapped fire hydrant might have done so. It can be difficult to infer the past from the present because there are many possible causes of a given effect.
West Virginia's former "intelligent design" bill passes the Senate - National Center for Science Education
West Virginia's former "intelligent design" bill passes the Senate.
Posted: Fri, 26 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
As British astrophysicist Fred Hoyle put it, the fine-tuning of the laws and constants of physics suggested that a designing intelligence “had monkeyed with physics” for our benefit. As one of the architects of the theory of intelligent design and the director of a research center that supports the work of scientists developing the theory, I know that it isn’t. And recently, a major conference about intelligent design was held in Prague (attended by some 700 scientists, students and scholars from Europe, Africa and the United States), further signaling that the theory of intelligent design has generated worldwide interest. In spite of the claims of evolutionary psychologists, many of humanity’s most impressive charitable, artistic, and intellectual abilities outstrip the basic requirements of natural selection.
To attribute design to an organism one need not demonstrate that every aspect of the organism was designed. Organisms, like all material objects, are products of history and thus subject to the buffeting of purely material factors. Automobiles, for instance, get old and exhibit the effects of corrosion, hail, and frictional forces.
That is, whenever we see systems that have the feature of irreducible complexity and we know the causal story about how such systems originated, invariably “intelligent design” played a role in the origin of such systems. Thus, Behe infers intelligent design as the best explanation for the origin of irreducible complexity in cellular molecular motors and circuits based upon what we know, not what we do not know, about the causal powers of intelligent agents and natural processes, respectively. Johnson reminded readers that Darwinism does not just claim that evolution (in the sense of change over time) has occurred.
Why do you think some people do not accept evolution?
Religious scholars in the past had struggled with such dysfunction and cruelty because they were difficult to explain by God’s design. In the 18th and 19th centuries and until the introduction of Darwin's theory of evolution, the "argument from design" was the prevailing view of the origins of the natural world. The radio astronomers in "Contact" detected design in a radio signal when they discovered its pulses reflected all and only the prime numbers from 2 to 101. This signal had specified complexity, and Ellie Arroway and crew took this as evidence of intelligent design. The scientific community responds to irreducible complexity by stating that while it is true that natural selection can only choose among traits that are already functioning, the traits don't have to be functioning in their current form.
Our minds recognize the effects of other intelligent beings when we see the purposeful arrangement of parts, such as the letters and words in a book. We know from our own experience that such things as books and art only come from one source, a mind. So, when we see intentionally designed systems, purposeful arrangement of parts, we know that at an intelligent agent, a mind, must be the cause.
That’s quite a job description — one that no known material cause or set of material causes appears capable of accomplishing. The need for such a powerful and intelligent first cause strongly suggests a purposeful design behind the origin of the universe. The central issue is how biological complexity emerged and whether intelligence played a pivotal role in its emergence. The Law of Conservation of Information was created by William Dembski and involves some very detailed and complex mathematical equations. At its most basic, Dembski's law states that nature cannot create new information (as in information contained in DNA); it can only work with the information it already has.
In its quantitative form -- the Explanatory Filter -- it can be applied to scientific questions as successfully as it is applied to questions that arise in everyday life. So we need other people to form the thick edge of the wedge to take on the questions that do require a scientific expertise. Like a professor of biochemistry, Michael Behe, and a mathematician and philosopher of science, William Demsky. They have to take up other questions that arise and do some of the job that I'm not well-equipped to do after I've got things going with my arguments from logic and evidence.
I think they want to do what I set out to do when I first crafted the intelligent-design movement—to come out with a position that was not so enormously different from current orthodoxy that it couldn't be discussed but was different enough that it was really upsetting. In the end, I think I came up with something that was even more upsetting than I thought it was going to be. That's one of the questions I examined when I first took up the story. Are the people ignorant and prejudiced, or are they seeing something that the experts might have missed? But also in the course of all your expert training, you pick up a worldview and a set of prejudices that you then become completely dependent on in order to continue to be an expert.

Both claims are scientifically testable using the standard methods of science. But ID theorists say that when we use the scientific method to explore nature, the evidence points away from blind material causes, and reveals intelligent design. Hume’s objections to the classical design argument fail to refute the argument of this book for several reasons.
It's not just that if they get the cell then everything else will be easy. But it was thought in Darwin's day that the cell was no problem at all. How do you get from cells to complex animals and then to apes, and from apes to human beings?
I foresee the day when Darwinian evolution will be taught at universities in courses on British intellectual history, and biology will have moved on. When I speak to audiences about this, I like to say that even the Darwinian theory of evolution is valid up to a point. The problem with the theory of evolution is not that it's altogether wrong, but that it's correct only in a very limited and relatively trivial sphere rather than as the grand creation story that it is made out to be. It's a good theory for how finch beaks vary in size or how disease-causing microorganisms become resistant to antibiotic medicines. It's true that supernatural causes are a subject outside of science. But intelligent versus unintelligent causes is a subject very much within science.

No comments:
Post a Comment